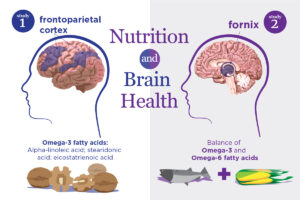
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega 3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is essential for the human body. They are considered essential because the body cannot produce them on its own, so they must be obtained from the diet. There are three main types of omega 3 fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
EPA and DHA are primarily found in fatty fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, while ALA is found in plant sources, such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These fatty acids play a crucial role in brain function, as well as normal growth and development.
Omega 3 fatty acids have been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cholesterol levels, and reducing inflammation in the body. They are also important for maintaining healthy brain function and have been linked to a reduced risk of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
In addition, omega 3 fatty acids are important for eye health, as DHA is a major structural component of the retina. Overall, omega 3 fatty acids are an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Brain Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that are crucial for overall health, but they play a particularly important role in brain health. These polyunsaturated fats are known for their anti-inflammatory properties and have been linked to various benefits for the brain, including improved cognitive function, reduced risk of neurodegenerative disorders, and better mood regulation.
One of the key reasons why omega-3 fatty acids are so important for brain health is their role in brain development. During pregnancy and early childhood, these fatty acids are crucial for the growth and development of the brain and nervous system. Studies have shown that adequate intake of omega-3s during this critical period can have long-lasting effects on cognitive function and behavior.
Furthermore, omega-3 fatty acids have been found to have a positive impact on cognitive function in adults as well. Research suggests that regular consumption of omega 3 fatty acids may help improve memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities, making them important for maintaining brain health as we age.
Overall, incorporating sources of omega-3 fatty acids into your diet, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can have significant benefits for your brain health. Whether you’re looking to support brain development in young children, maintain cognitive function in adulthood, or reduce the risk of neurodegenerative disorders, omega 3 fatty acids are an essential nutrient for overall brain health.

How Omega-3 Fatty Acids Affect Brain Development
Omega 3 fatty acids play a crucial role in the development of the human brain. These essential fatty acids are vital for promoting healthy brain growth and function, particularly during the early stages of life. Studies have shown that omega 3 fatty acids, specifically docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are essential for proper brain development in infants and young children.
During pregnancy, omega 3 fatty acids are transferred from the mother to the fetus to support the growth and development of the baby’s brain. The presence of DHA in breast milk also continues to provide essential nutrients for brain development during infancy. In fact, DHA makes up a significant portion of the brain’s structural fats and is crucial for the growth of neural connections and synapses.
Furthermore, omega 3 fatty acids continue to play a crucial role in brain development throughout childhood and adolescence. These healthy fats support cognitive function, memory, and learning, all of which are essential for a child’s academic and social development. Research has also suggested that adequate intake of omega 3 fatty acids may have a positive impact on reducing the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as ADHD and autism.
In conclusion, omega 3 fatty acids are essential for brain development at every stage of life. From supporting fetal brain growth and development to promoting cognitive function and reducing the risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in children, the benefits of omega 3 fatty acids for brain development are undeniable.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cognitive Function
Omega 3 fatty acids play a crucial role in cognitive function and brain health. Research has shown that these essential fatty acids, including docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are important for maintaining healthy brain function and preventing cognitive decline.
Studies have indicated that omega 3 fatty acids can improve cognitive function in both children and adults. DHA, in particular, is concentrated in the brain and has been linked to improved memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
Furthermore, omega 3 fatty acids have been found to play a role in reducing the risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of these fatty acids help to protect the brain from age-related cognitive decline.
Incorporating omega 3 fatty acids into your diet through sources such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts can have a significant impact on cognitive function and overall brain health. Additionally, supplementing with fish oil or algae oil can be beneficial for those who may not consume enough omega-3-rich foods on a regular basis.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Mood Regulation
Omega 3 fatty acids play a crucial role in regulating mood and emotional well-being. Research has shown that consuming omega-3 rich foods or supplements can have a positive impact on mental health, helping to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Studies have found that individuals with higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids in their diet are less likely to experience mood disorders. This is thought to be due to the role of these fatty acids in regulating neurotransmitters in the brain, such as dopamine and serotonin, which are known to influence mood.
In addition to their impact on neurotransmitters, omega 3 fatty acids also have anti-inflammatory properties that may contribute to their mood-regulating effects. Chronic inflammation has been linked to an increased risk of depression, and omega 3 fatty acids have been shown to reduce inflammation in the body.
It’s important to note that while there is evidence supporting the role of omega 3 fatty acids in mood regulation, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind this relationship. Nevertheless, incorporating omega-3 rich foods, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, into a balanced diet may offer potential benefits for mental well-being.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neurodegenerative Disorders
Neurodegenerative disorders are a group of conditions characterized by the progressive degeneration of the structure and function of the nervous system. These disorders can have a devastating impact on an individual’s quality of life, often leading to cognitive decline, loss of motor function, and eventually, death. Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease are examples of neurodegenerative disorders that affect millions of people worldwide.
Research has shown that omega-3 fatty acids may play a role in the prevention and management of neurodegenerative disorders. Specifically, the two most important types of omega 3 fatty acids, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), have been found to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties that could potentially slow the progression of these conditions.
Studies have suggested that individuals who consume higher levels of omega 3 fatty acids may have a reduced risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders. In addition, some research has indicated that omega 3 fatty acids may help improve cognitive function and reduce the severity of symptoms in those already affected by these conditions.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between omega 3 fatty acids and neurodegenerative disorders, the existing evidence suggests that incorporating sources of these essential fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, into one’s diet may have potential benefits for brain health and the prevention of these debilitating conditions.
Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Brain Health
Omega 3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in brain health. They are important for cognitive function, mood regulation, and can even help in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative disorders. It’s important to include omega 3 fatty acids in your diet to support optimal brain function.
One of the best sources of omega 3 fatty acids is fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines. These fish are rich in both EPA and DHA, which are two types of omega 3 fatty acids that are particularly beneficial for brain health. Consuming fatty fish at least twice a week can provide you with an adequate amount of omega 3 fatty acids.
In addition to fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are also good sources of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a type of omega-3 fatty acid. ALA can be converted into EPA and DHA in the body, making these plant-based sources beneficial for brain health as well.
If you’re not a fan of fish or plant-based sources, you can also consider taking omega-3 supplements. These supplements are available in the form of fish oil, algae oil, or krill oil, and can provide you with a concentrated dose of omega 3 fatty acids to support brain health.
You can also read our article about minerals and vitamins for health